Caching is an important tool in your toolbox as a developer. When used correctly in can vastly improve performance. However don't introduce caching blindly, it is crucial to monitor your cache usage to see if your caching strategy works and provides the benefits you expect.
With .NET 7 this became a little bit easier, thanks to the introduction of MemoryCacheStatistics that holds cache hits, misses, and estimated size for IMemoryCache.
You can get an instance of MemoryCacheStatistics by calling GetCurrentStatistics() on your IMemoryCache. instance when the flag TrackStatistics is enabled.
If you construct the IMemoryCache instance yourself you can do this by specifying it through the MemoryCacheOptions object:
Or if you are using Dependency Injection, you can do this:
Now I can create my own EventSource implementation that reads the data from the MemoryCacheStatistics:
I created a small console application that reads and writes some value to an IMemoryCache instance and uses this EventSource:
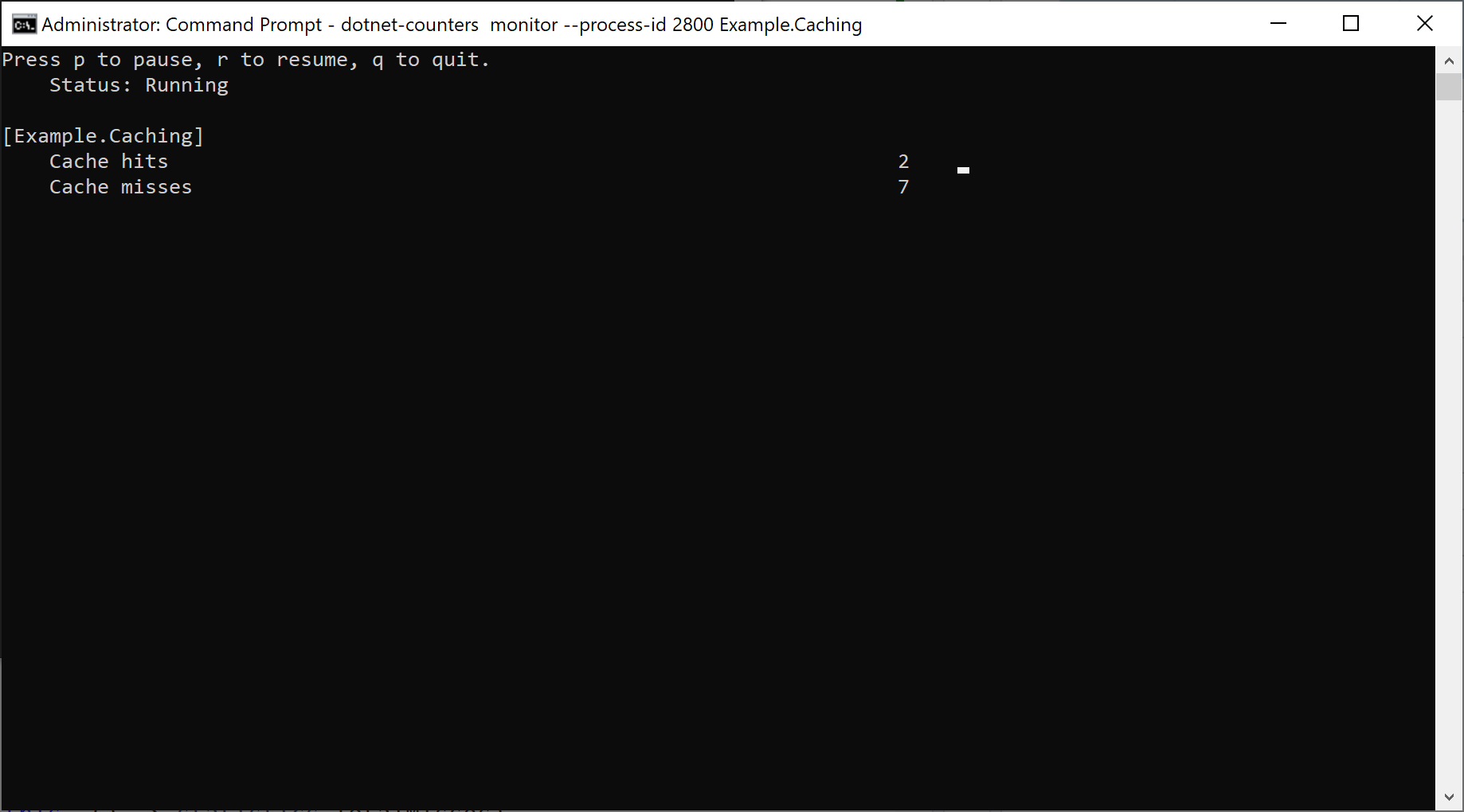
Let's have a look at the values we get back through the dotnet-counters tool:
Remark: If you want to learn on how to use the dotnet-counters tool, you can have a look at one of my earlier posts.