By default when running an ASP.NET Core application in IIS, the application will not be started until the first user hits your ASP.NET Core application. This of course saves some resources(CPU, memory,...) when no one is accessing your site, but comes with a performance penalty when the first request arrives.
A related feature exists where the application pool is shutdown after some idle time.
Although I think this is a good default it is not what we want when we have one or more background tasks running in our ASP.NET Core application. In these situations you want to have your ASP.NET Core application always running.
Let me walk you through the steps how to get this done.
Install IIS features
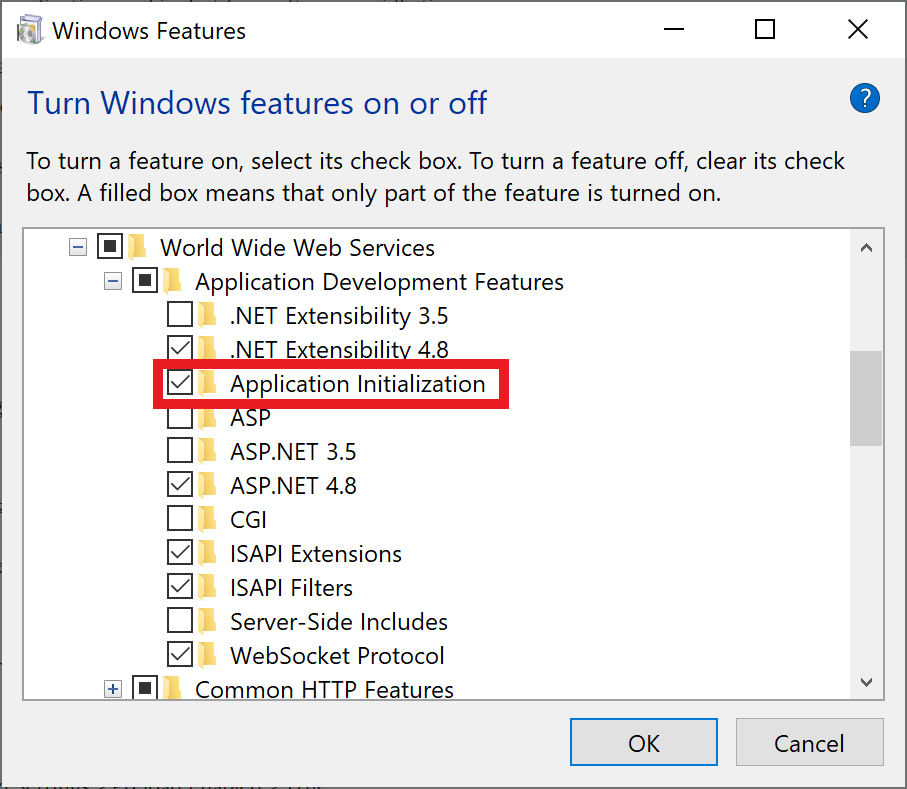
First check if you have the Application Initialization Module installed in IIS. If you are doing this on your local development machine, have a look at the list of Windows Features:
Otherwise you can install it through Server Manager:
- Open the Add Roles and Features Wizard.
- In the Select role services panel, open the Application Development node.
- Select the checkbox for Application Initialization.
Configure IIS
Now we need to configure IIS. Start by opening the IIS Manager.
We start by configuring the Application pool:
- Select Application Pools in the Connections panel.
- Right-click the app's app pool in the list and select Advanced Settings.
- The default Start Mode is
OnDemand. Set the Start Mode toAlwaysRunning. - Also update the Idle Time-Out (minutes) to 0.
- Select OK.
Now we need to also update the website to activate the preload feature:
- Open the Sites node in the Connections panel.
- Right-click the app and select Manage Website > Advanced Settings.
- The default Preload Enabled setting is
False. Set Preload Enabled toTrue. - Select OK.
Configure your ASP.NET Core app
There is not much you need to do at the level of your ASP.NET Core application. The only thing that is required is that your are using the In-Process hosting model which is the default.
More information can be found at: