Visual Studio supports staging files from the moment Git support was introduced and most of the time that is sufficient. But sometimes it can be useful to stage chunks of changes in a file instead of a complete file. This feature (also known as interactive staging) was introduced in Visual Studio 2022 v17.2. I never used the feature before so let's see how this works...
Git line staging is still marked as a preview feature but if you are using Visual Studio 2022 v17.2 or higher, it should be enabled by default.
The first thing you should notice when line staging is enabled, is that individual changes are visible in the editor margin. Added, edited or deleted lines are all shown using a different color and annotation:
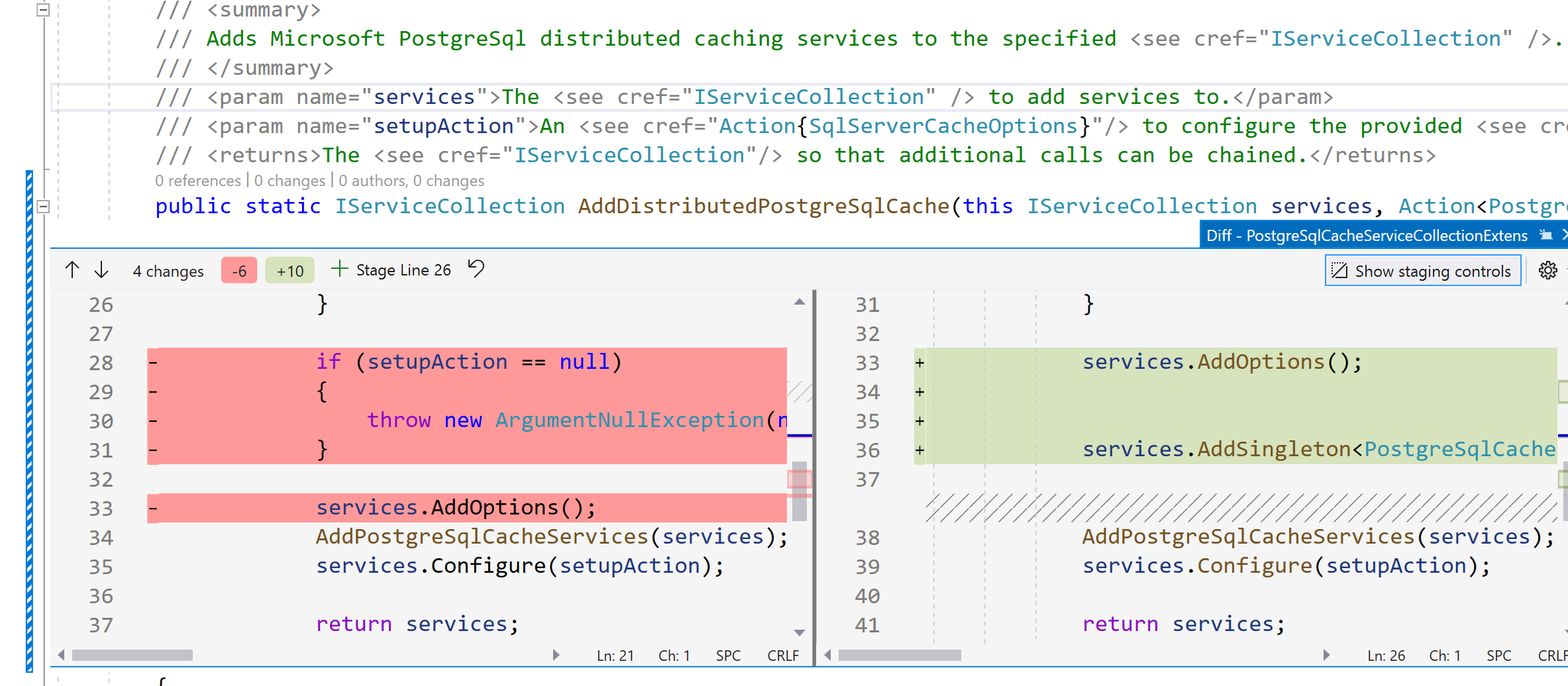
If we now click on a color margin, an inline Peek Difference view is opened.
Now you can stage the selected change by clicking on the + Stage Line <LineNumbers> button:
You can also select one or more lines in the Peek Difference view, right click and choose Git –> Stage selected Range to only stage your selection.
Another option is to go to the Git Staging window and choose Compare with Unmodified:
Here you can hover over a specific change and choose + Stage Change:
If you want to stage a specific line, click on a specific line and choose + Stage Line:
Nice!
Remark: At the moment of writing this post, the Visual Studio 2022 v17.6 preview 1 was released that introduced support for unstaging specific lines.
More information: Line-staging (Interactive Staging) - Visual Studio Blog (microsoft.com)