Testing a token-protected API can be a challenge. You need to have an identity and access management solution in place to get a valid access token that can be passed to your API.
.NET 7 makes this whole process easier by introducing a new command line tool; user-jwts. This allows you to generate JSON Web Tokens that can be used during development.
Let me walk you through the steps to use this new tool.
Getting started with user-jwts
I have an existing ASP.NET Core application configured to use JTW Bearer authentication:
I introduce a new endpoint that requires authorization:
Before .NET 7 to be able to test this endpoint, we need to register this API in your IAM solution and log in by providing valid credentials. Not impossible to do, but still a lot of work...
Let’s invoke the user-jwts tool:
dotnet user-jwts create
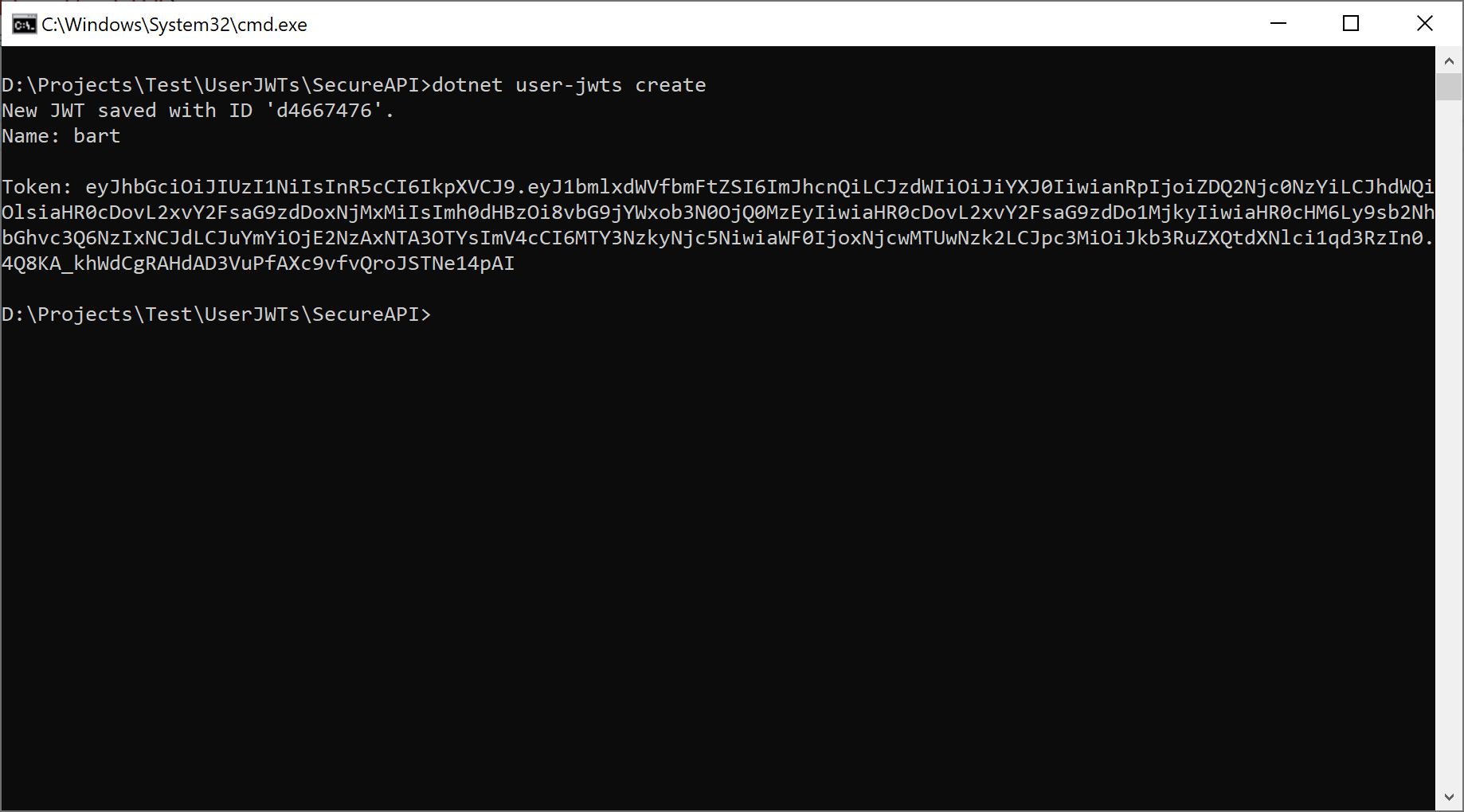
Executing this command will result in the following actions:
- A JWT token is created and stored as a ‘user secret’ on your local machine.
- The appsettings.development.json is updated with the necessary configuration details:
Now we can call our API by passing the generated JWT token:
curl -i -H "Authorization: Bearer {token}" https://localhost:7214/secret
If you want to create a token for a specific user and scope, you can do that as well:
dotnet user-jwts create –name Bart --scope "openid" –scope "profile"
You can find the complete example app here: https://github.com/wullemsb/UserJwtsDemo
If you want to learn more, check out the documentation: Generate tokens with dotnet user-jwts | Microsoft Learn

