With NuGet 6.0, a new feature Package Source Mapping was introduced. Goal of this feature is to help improve security by safeguarding your software supply chain.
What is Package Source Mapping?
If I want to explain what Package Source Mapping is, I should start by explaining the concept of a Package Source. In NuGet a Package Source is the source where nuget searches for packages. This can a public source(like nuget.org) and/or a private source(like Azure Artifacts or a local disk).
You can add a package source by executing the following command:
dotnet nuget add source <source> –n MySource
It is possible to define multiple sources. By default when multiple sources are defined nuget will scan all configured package sources to find and restore a specific package. This introduces a risk as you are not sure where a specific package is coming from.
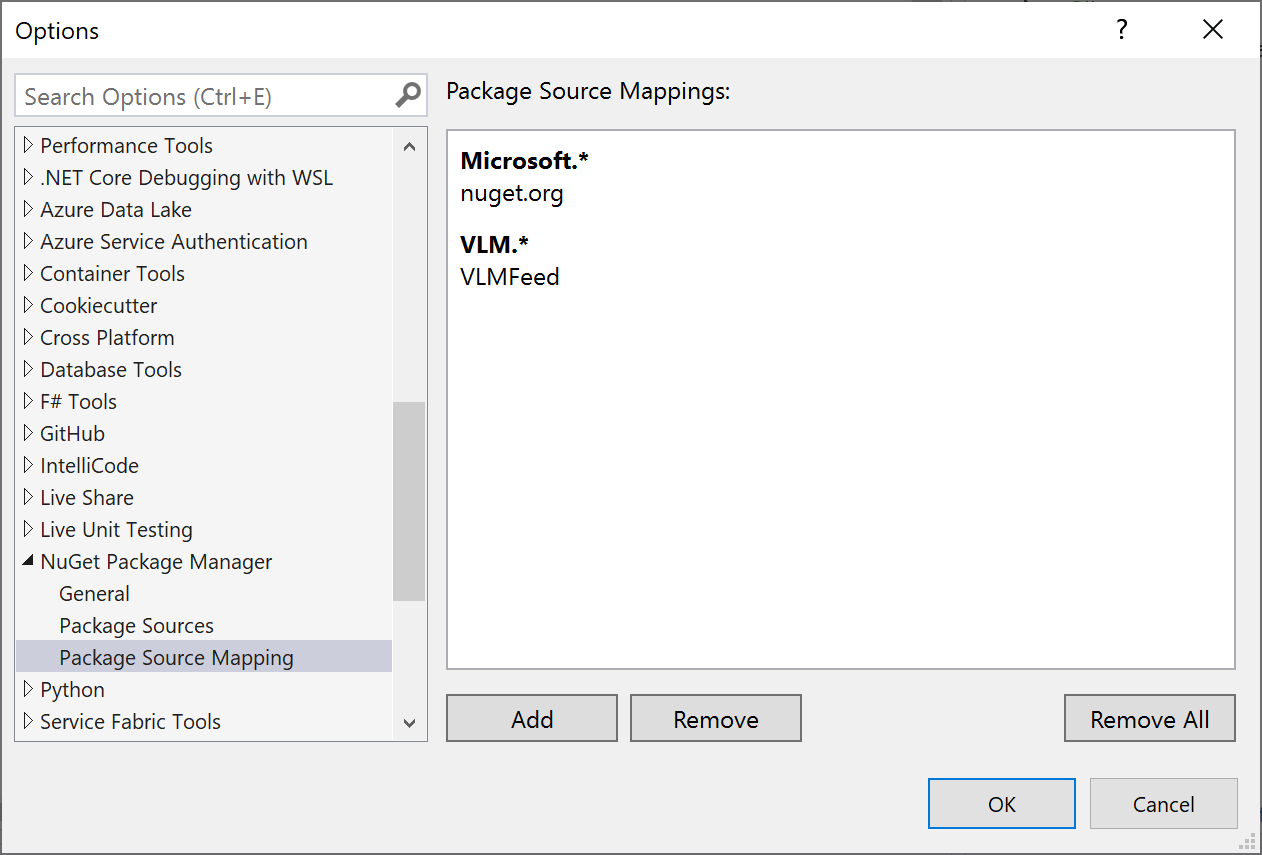
A risk that can be mitigated by using Package Source Mapping(PCM). PCM allows to centrally declare which source each package in your solution should restore from in your nuget.config file.
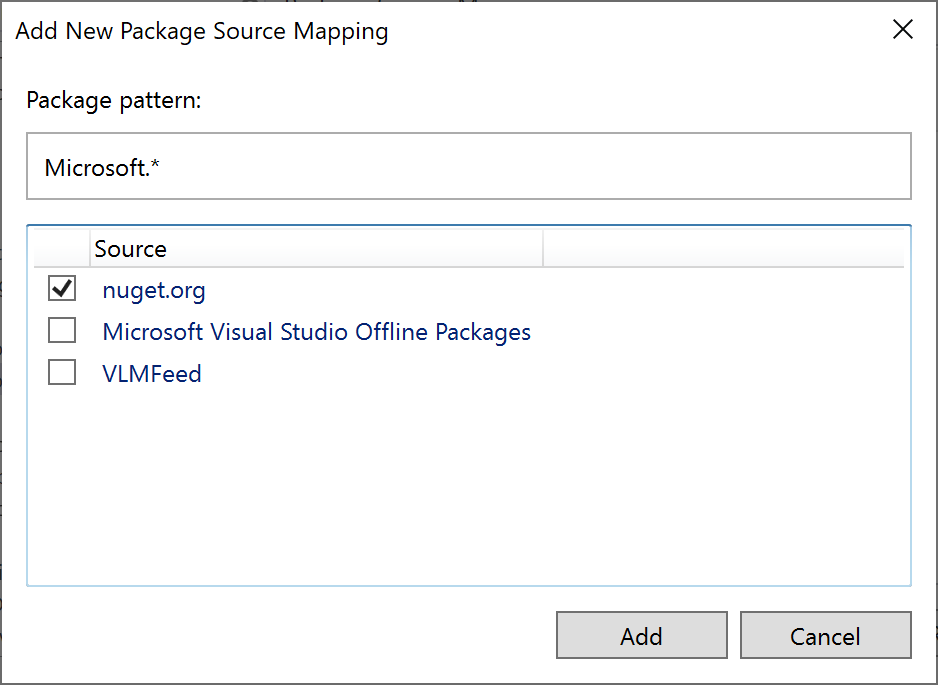
You can configure Package Source Mapping directly in the Visual Studio IDE. For each mapping you need to specify a pattern and one or more package sources:
This will update your nuget.config file like this:
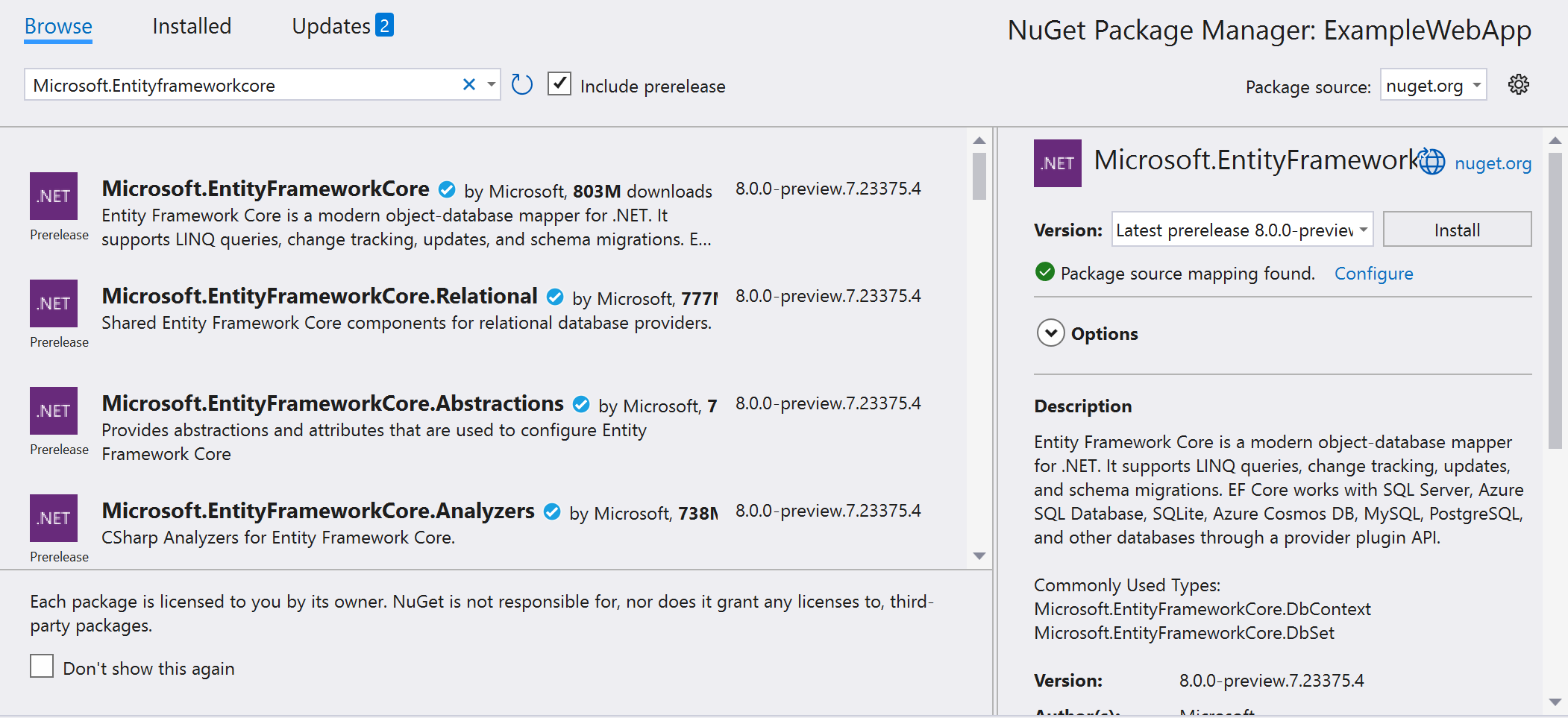
Starting from NuGet 6.7 this got improved even further as you can easily see when NuGet packages are (not) mapped to respective package source(s):
More information:
Announcing NuGet 6.7 – Keeping You Secure - The NuGet Blog (microsoft.com)
Package Source Mapping | Microsoft Learn
dotnet nuget add source command - .NET CLI | Microsoft Learn