For an Azure Fabric based data platform we are building I'm evaluating PowerBI as a possible reporting solution. My knowledge of PowerBI is almost non existant so there are a lot of things I learned along the way.
Yesterday I talked about the different data fetching strategies. Today I want to focus on how to limit the amount of data.
I explained yesterday that PowerBI can handle large amounts of data. This is good news but during development I want to work with a smaller dataset to limit the file size and gain some extra development speed.
Limit the amount of data
Let’s find out how we can get limit the amount of data in PowerBI.
Start by opening the Query Editor view in PowerBI by selecting Transform data from the Home tab:
This will load the Query Editor.
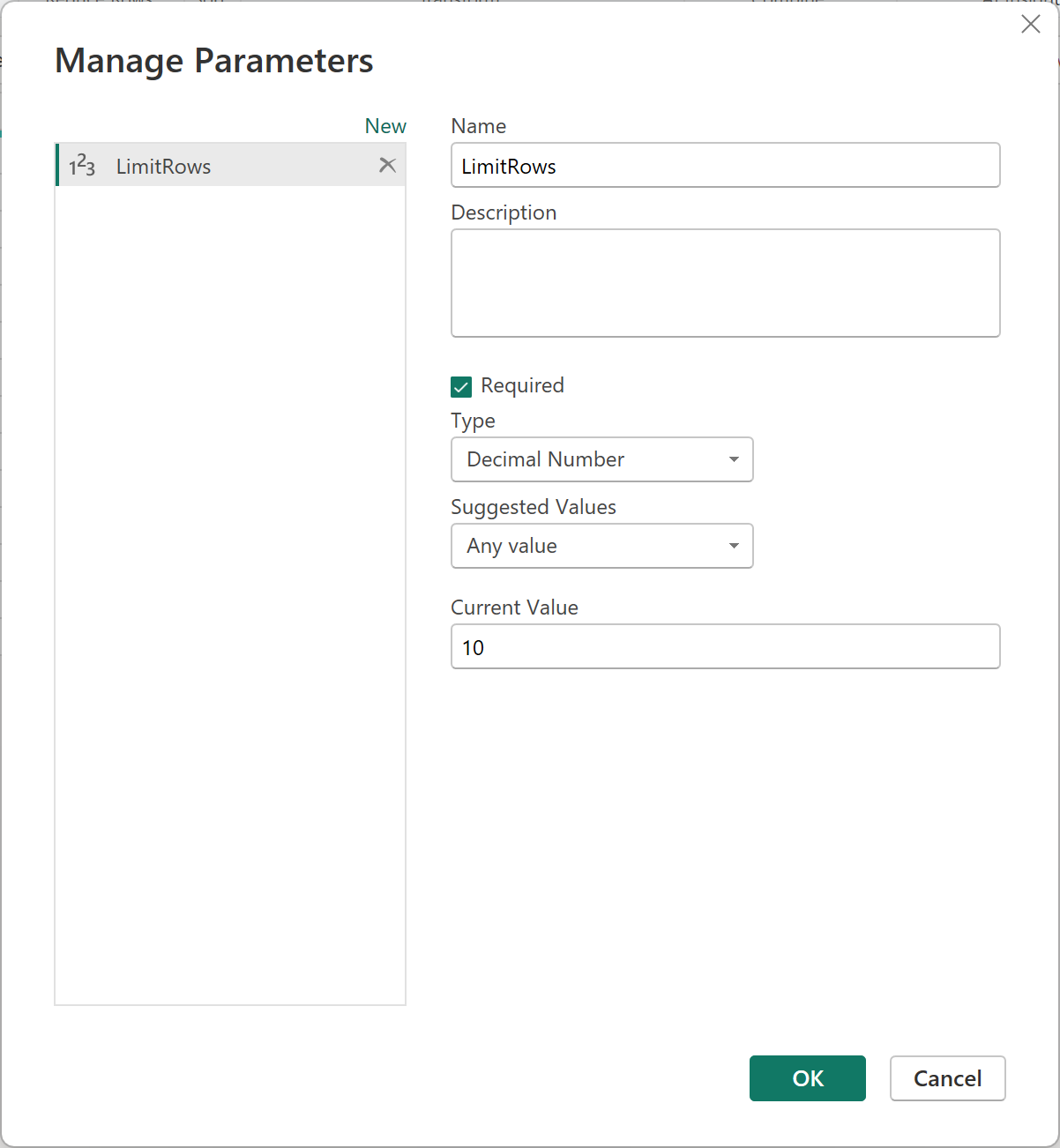
Here we need to create a new parameter that can be used as a limit value. Click on Manage Parameters and choose New Parameter:
We create a LimitRows parameter with a default value of 10:
Now that we have this parameter we can update our PowerQuery and introduce an extra step to limit our dataset.Therefore we open the Advanced Editor available in the Query pane:
Here we can update our query and implement the following logic:
- If our parameter is less than or equal to 0 then return all the rows, otherwise
- If our parameter is more than 0 then return that number of rows from the table
We change the existing query and introduce an extra step in the data pipeline:
Click on Done to apply the updated query and introduce the extra step:
Remark: This is a contrived example as our source is a JSON file but this can also be used when querying other sources(like a database).