So far my ‘go to’ approach for using language models locally was through Ollama and Semantic Kernel. With the announcement of Foundry Local at Build, I decided to try to combine AI Foundry Local with Semantic Kernel.
Time to dive in…
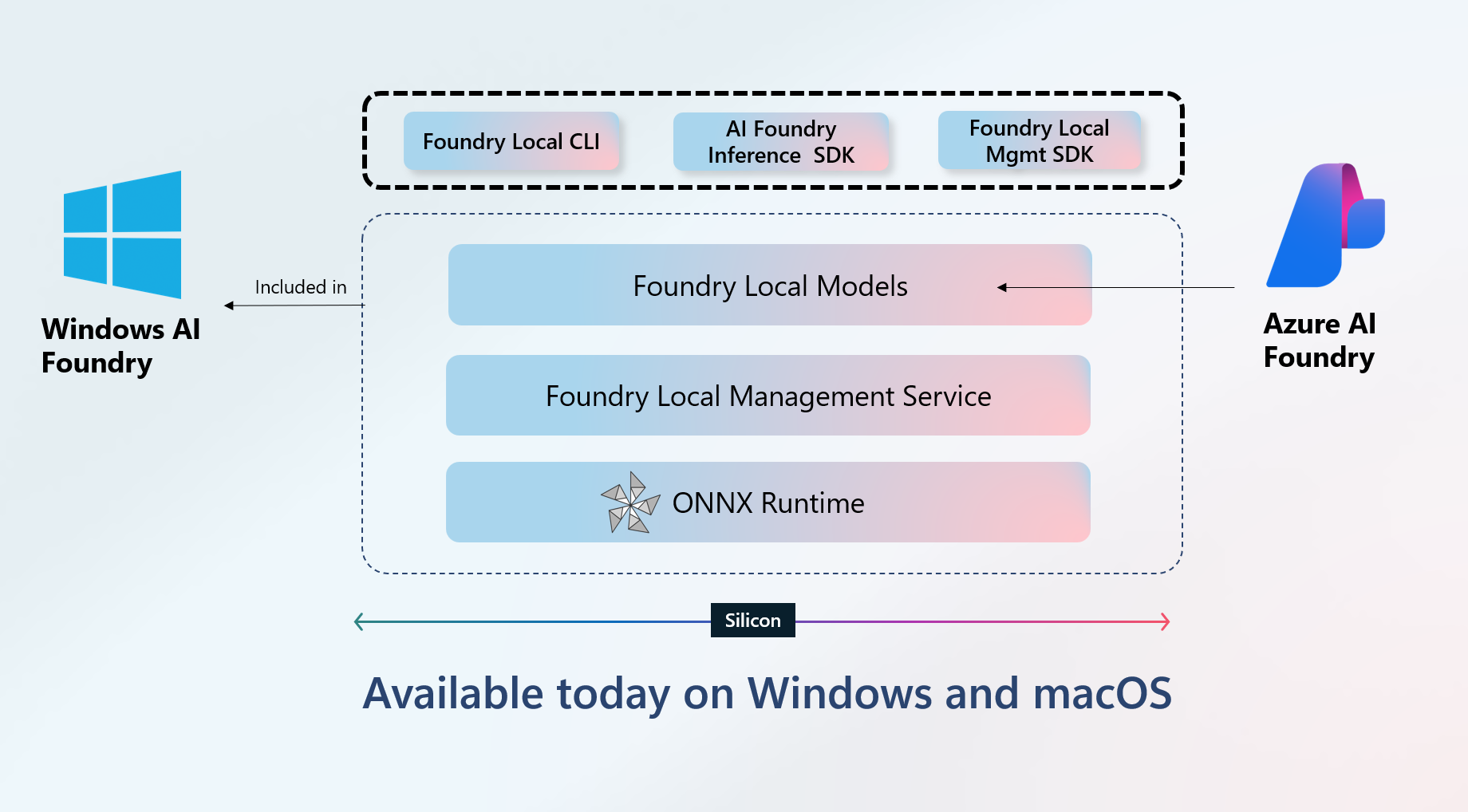
What Is Foundry Local?
Foundry Local is Microsoft’s local execution runtime for large language models. Unlike cloud-hosted models, Foundry Local runs entirely on your device, giving you privacy, customization, and cost-efficiency. Thanks to its simple CLI and REST API, it integrates smoothly into existing workflows and can support a variety of models and use cases.
The easiest way to get started with Foundry Local is through winget:
winget install Microsoft.FoundryLocal
Once Local Foundry is installed, you can request the list of available models:
foundry model list
Download the model you want to use:
foundry model download phi-3.5-mini
Now you can run foundry using the downloaded model:
foundry model run phi-3.5-mini
If you forgot, the models you already have in cache, you can check this using following command:
foundry cache list
Once the model is running, you can start asking questions:
Use your Foundry Local model in Semantic Kernel
Start by running Foundry Local in service mode:
foundry service start
This will expose an OpenAI API compatible endpoint on http://localhost:5273. We’ll use this endpoint in our application.
Create a new console application and add a reference to Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.OpenAI:
dotnet package add Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.OpenAI
Next thing you need to do is to configure the OpenAI connector to use the local model:
Remark: Notice that we add a v1 to the URL and use the model id
The remaining part of you Semantic Kernel code should remain the same:
Let’s run the app to verify that it works: