The last 2 weeks we had some production issues where an unexpected 401 message was returned from our IIS servers. To further investigate the issue, I got an old tool out of the dust; Log Parser Studio.
Log Parser Studio is a utility that allows you to search through and create reports from your IIS, Event, EXADB and others types of logs. It builds on top of Log Parser 2.2 and has a full user interface for easy creation and management of related SQL queries.
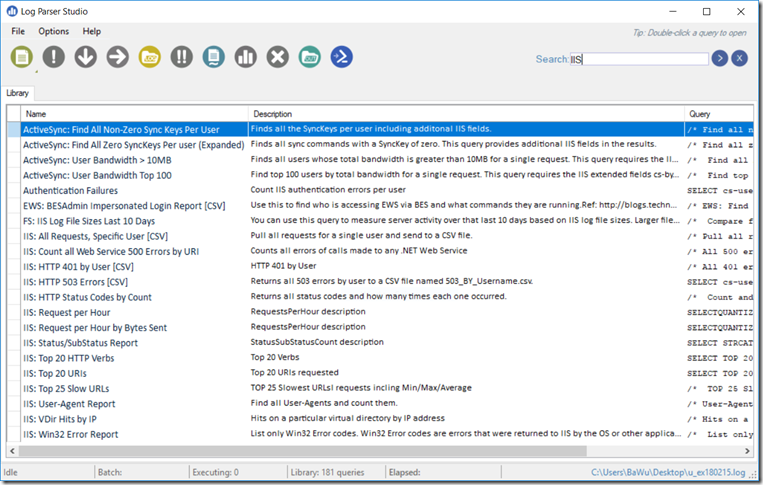
Log Parser Studio allows to query all kinds of log files using a SQL like syntax. It comes out of the box with a large list of sample queries that can help get started.
How to use it
- Open Log Parser Studio(LPS.exe)
- Click on the New Query button or choose one of the queries from the library
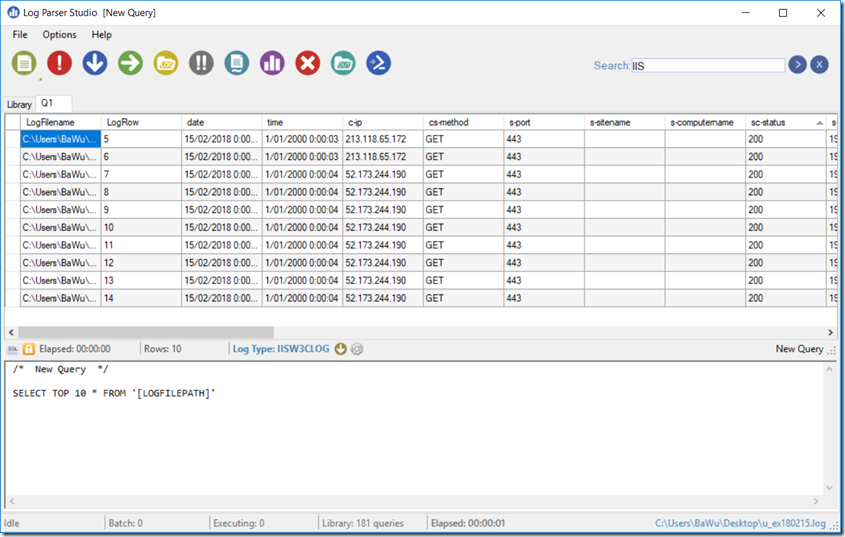
- A new query window appears
- Now it is time to first specify the LogType. Click on the Log Type link in the middle and choose the correct type from the list:
- Next we have to select the files to query. Click on the Choose Files/folders icon
- The Log File Manager window appears. Here you can use Add Files or Add Folders to add log files.
- After selecting some files, click OK to return to the Main screen.
- Now it is finally time to execute the query. Click on the Execute button
- After some time(depending on the number of log files and the complexity of the query), the query results are returned: