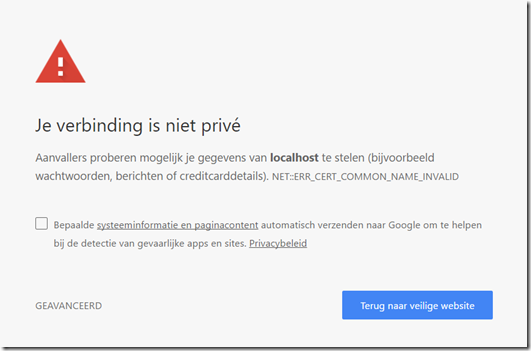
If you are a developer and are using a Self-Signed certificate for your HTTPS server, you recently may have seen the following error in Chrome(or a non-Dutch equivalent ):
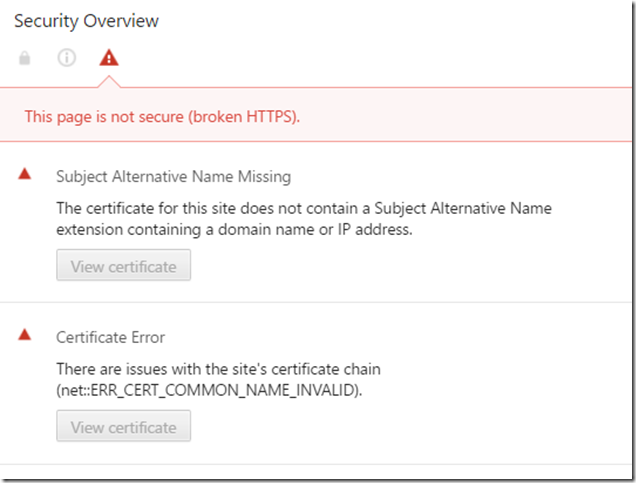
Starting from Chrome 58 an extra security check got introduced that requires certificates specify the hostname(s) to which they apply in the SubjectAltName field. After they first introduced this change, the error message was not very insightfull but today if you take a look at the Advanced section of the error message or the Security panel in the Developer tools, you’ll get some more details pointing to the SubjectAltName issue:
Create a new self-signed certificate
To fix it, we have to create a new self-signed certificate. We can not use the good old makecert.exe utility as it cannot set the SubjectAltName field in certificates. Instead, we’ll use the New-SelfSignedCertificate command in PowerShell:
New-SelfSignedCertificate ` -Subject localhost ` -DnsName localhost ` -KeyAlgorithm RSA ` -KeyLength 2048 ` -CertStoreLocation "cert:CurrentUser\My" ` -FriendlyName "Localhost certificate"
Now you have a new certificate with a correct Subject Alternative Name in your Personal certificate store:Next step is to trust this certificate by moving it to the Trusted Root Authorities. You can either do this by hand using the certmgr tool in Windows or script it with Powershell as well:
# set certificate password here $pfxPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "YourSecurePassword" -Force -AsPlainText $pfxFilePath = "c:\tmp\localhost.pfx" $cerFilePath = "c:\tmp\localhost.cer" # create pfx certificate Export-PfxCertificate -Cert $certificatePath -FilePath $pfxFilePath -Password $pfxPassword Export-Certificate -Cert $certificatePath -FilePath $cerFilePath # import the pfx certificate Import-PfxCertificate -FilePath $pfxFilePath Cert:\LocalMachine\My -Password $pfxPassword -Exportable # trust the certificate by importing the pfx certificate into your trusted root Import-Certificate -FilePath $cerFilePath -CertStoreLocation Cert:\CurrentUser\Root
Import it in IIS
OK, almost there. A last step to get it working in IIS is to import the pfx in IIS:
- Open IIS using inetmgr.
- Go to Server Certificates.
- Click on the Import… action on the right. The Import certificate screen is shown.
- Select the pfx, specify the password and click OK.
- Now that the certificate is available in IIS, you can change the bindings to use it. Click on the Default Web site(or any other site) on the left.
- Click on the Bindings… action on the right. The Site Bindings screen is shown.
- Click on the https item in the list and choose Edit… . The Edit Site Binding screen is shown.
- Select the newly created SSL certificate from the list and click OK.