Yesterday I blogged about Azure Functions and how the Visual Studio tooling can make your life easier. But the guys at Amazon are not sleeping and I noticed that they added support for C# as well.
Note that the AWS Lambda functions in C# are using the .NET Core 1.0 runtime. Similar to Microsoft, you get full tooling support thanks to the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio.
- Install the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio.
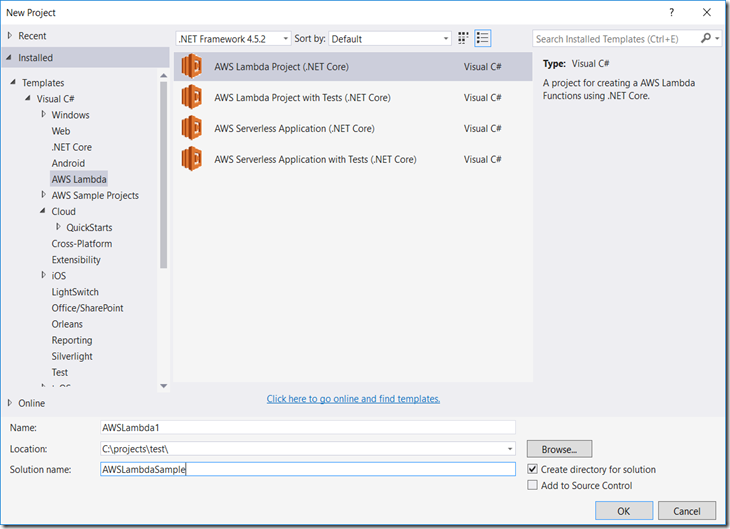
- Open Visual Studio and create a new project. Choose the AWS Lambda Project template and click OK.
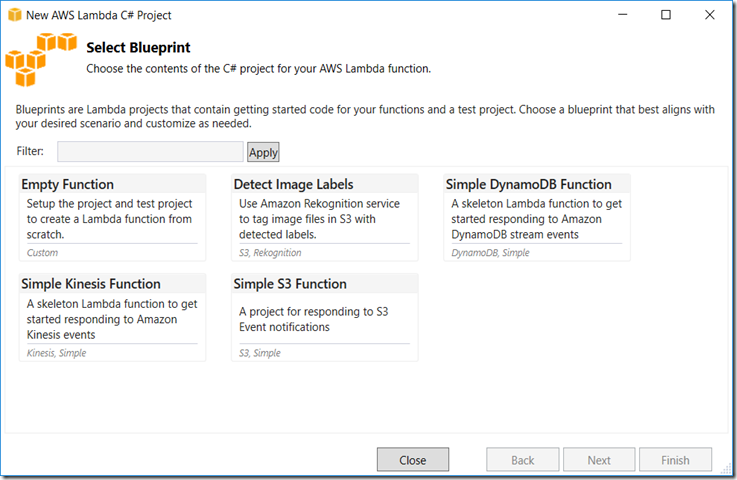
- Next step is to select a Blueprint.
- We choose the Simple S3 Function blueprint.
- You get a new project containing the following files
- aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json: . This file contains default values that the blueprint has set to help prepopulate some of the fields in the deployment wizard.
- Function.cs: Inside this cs file you can add your own logic.
- project.json: this is the default project.json for .NET core applications(will be replaced by a csproj file in the near future)
- The SDK is accompagnied by dotnet CLI integration. Open a command prompt and type dotnet lambda. Unfortunately I couldn’t find a way to debug locally.
More information at https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/developer/using-the-aws-lambda-project-in-visual-studio/