A colleague forwarded me a question about a failing build pipeline. When I took a look at the build results, I noticed that the Visual Studio Test task was failing.
Inside the logs I found more details explaining what was going on:
##[warning]No results found to publish.
##[debug]Processed: ##vso[task.logissue type=warning]No results found to publish.
##[error]System.Management.Automation.CmdletInvocationException: Unable to determine the location of vstest.console.exe ---> System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Unable to determine the location of vstest.console.exe
##[debug]Processed: ##vso[task.logissue type=error;]System.Management.Automation.CmdletInvocationException: Unable to determine the location of vstest.console.exe ---> System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Unable to determine the location of vstest.console.exe
at Microsoft.TeamFoundation.DistributedTask.Task.Internal.InvokeVSTestCmdlet.GetVsTestLocation()
at Microsoft.TeamFoundation.DistributedTask.Task.Internal.InvokeVSTestCmdlet.ProcessRecord()
at System.Management.Automation.CommandProcessor.ProcessRecord()
--- End of inner exception stack trace ---
at System.Management.Automation.Runspaces.PipelineBase.Invoke(IEnumerable input)
at System.Management.Automation.PowerShell.Worker.ConstructPipelineAndDoWork(Runspace rs, Boolean performSyncInvoke)
at System.Management.Automation.PowerShell.Worker.CreateRunspaceIfNeededAndDoWork(Runspace rsToUse, Boolean isSync)
at System.Management.Automation.PowerShell.CoreInvokeHelper[TInput,TOutput](PSDataCollection`1 input, PSDataCollection`1 output, PSInvocationSettings settings)
at System.Management.Automation.PowerShell.CoreInvoke[TInput,TOutput](PSDataCollection`1 input, PSDataCollection`1 output, PSInvocationSettings settings)
at Microsoft.TeamFoundation.DistributedTask.Handlers.LegacyVSTSPowerShellHost.VSTSPowerShellHost.Main(String[] args)
##[error]LegacyVSTSPowerShellHost.exe completed with return code: -1.
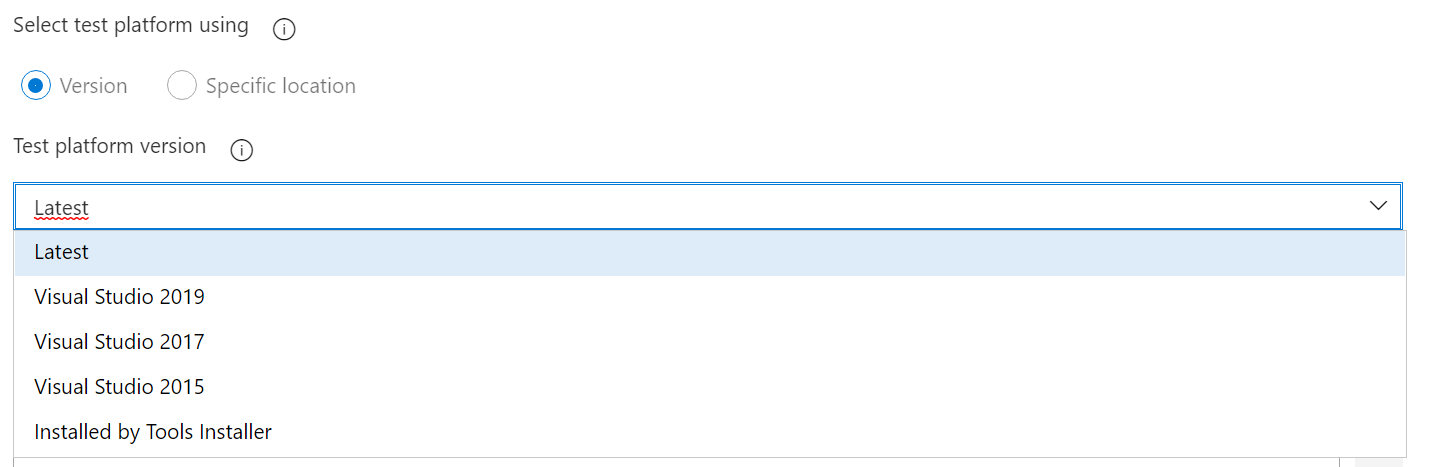
On the build server only the latest Visual Studio 2019 Build tools were installed. I noticed that he was still using an older Visual Studio Test Task version. This older version could only handle older Visual Studio version.
I changed it to the latest version:
Now I could select Visual Studio 2019(or latest) as the Test platform version:
I triggered the build again and this time it succeeded.