At one of my customers we are using WebDeploy for years to deploy our web applications to IIS. Although not that well documented, it works great and has good Visual Studio integration.
When reviewing the release pipeline of one of my colleagues I noticed that they introduced tasks in the release pipeline to stop the application pool before deploying the package and start the application pool again once the deployment completed.
This is probably done because ASP.NET Core applications hosted in IIS run in-place and lock the files that they are running from. So if we don’t stop the application pool, web deploy will fail as it cannot replace these files.
Although this solution works, WebDeploy has a built-in alternative; the EnableMsDeployAppOffline flag.
When set to true this flag, WebDeploy will create an app_offline.htm file which unloads the running application, publishes files, then removes that file.
Sidenote: About app_offline.htm
The app_offline.htm is a long existing feature in IIS that can be used to shut own the Application Host and start it back up but without loading any of the modules and only serving the app_offline.htm file.It is an effective way to keep your site from running and showing a ‘busy’ or ‘not available’ message instead. As long as this file is found in the root folder of your site no code will be run. Once the file gets deleted, the site starts back up.
When using the EnableMsDeployAppOffline flag, the app_offline.htm file is created for you by WebDeploy.
To use it through msbuild you need to add the following command line argument:
/p:EnableMSDeployAppOffline=true
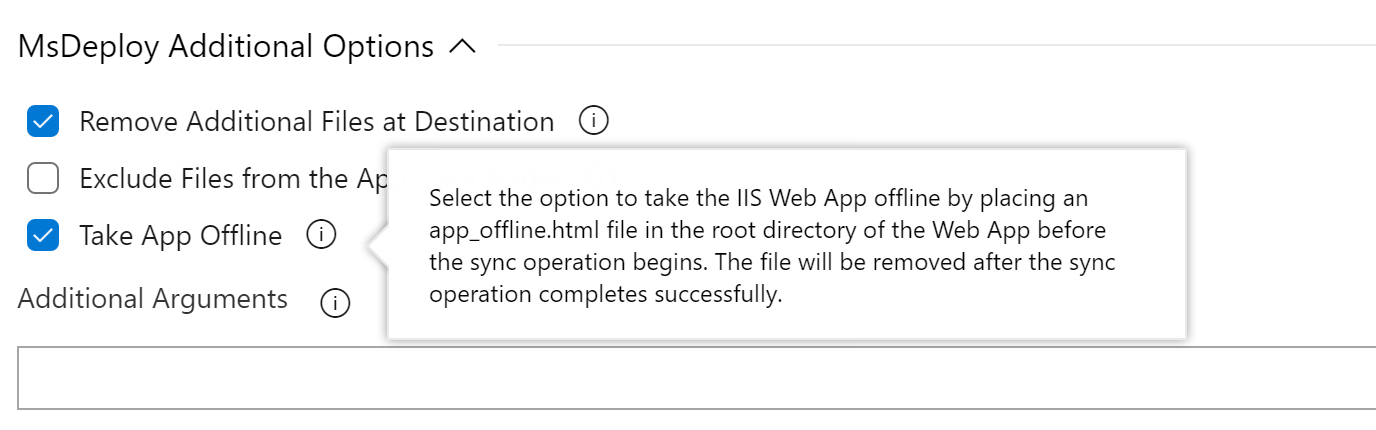
Or when using the WinRM – Web App Deployment tasks, you can set the Take App Offline flag: