The SQL Server Profiler has been around for a very long time. It is very useful if you are trying to see in real time what SQL queries are being executed against your database. However, in the SQL Server 2016, Microsoft announced that the SQL Profiler will be deprecated in future versions.
Does this mean that there are no profiling options left in SQL Server? Luckily no, the SQL Profiler will be replaced by Extended Events(XE). Extended Events works via Event Tracing (ETW) which consumes less resources and allows much more flexibility. It also can monitor more events than the Profiler.
Where can I find these Extended Events?
- Open SQL Server Management Studio( for SQL 2014 or higher) and connect to one of your Database instances
- Go to Management>Extended Events:
- Expand the Extended Events section, right click on Sessions and choose New Session Wizard
- The Session wizard will help us to select the events we want to profile. Click on Next >
- Specify a session name and click Next >
- Now you can choose an existing template. Leave the Do not use a template radiobutton checked and click on Next >
- The next screen is where the real work is done. Here you specify the events you want to monitor. Luckily you can search through them. Select some events you want to track and click Next >
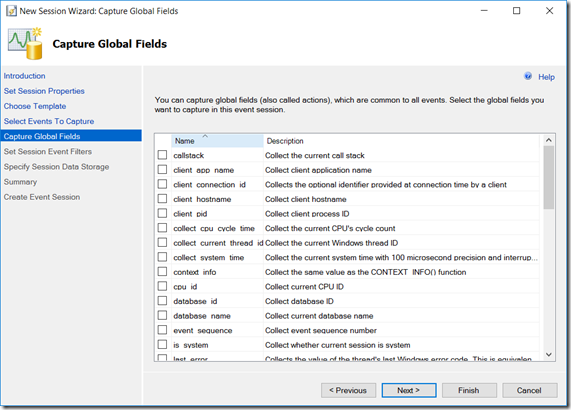
- Now you can specify any global fields(e.g. username, database name,…) you want to capture together with the events. Click Next > to continue
- Next step is to apply some optional filters to limit the amount of data that is returned. Click Next > to continue
- The session storage allows you to specify how to collect the data and store it. Click Next >.
- On the Summary you get an overview of the selected options. Click Finish to generate the Session.
- Note: There is an option to generate a script from this configuration. So you can re-use it later.
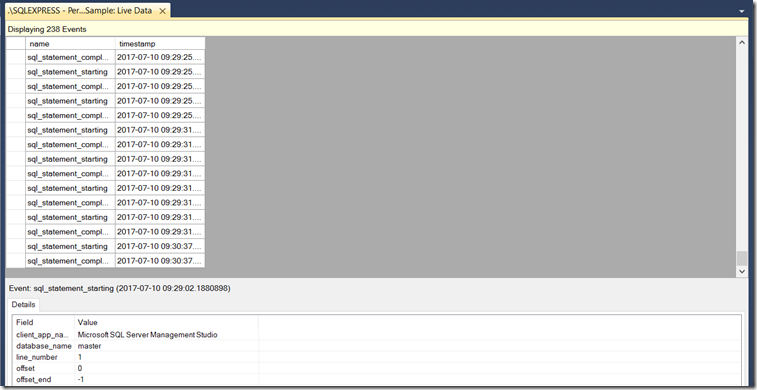
- After clicking Finish you end up on a Success page. Here you can start the session immediately and watch the data when it is captured.