Before I dive into the details on how to get Azure Arc up and running on your laptop, it would be a good idea to start with a short introduction.
Therefore we first have to dive in how Azure works. The hearth of the Azure ecosystem is the Azure control plane. This control plane manages all the resources you can find in Azure. It helps you to inventorize, organize and govern all resources and multiple tools exist that can help you to interact with it (think ARM templates, Bicep, Terraform, Pulumi, …)
You probably know this control plane better as the Azure Resource manager. It controls and manage all the Azure resources which can be as big as a Kubernetes cluster and as small as a static ip address. These resources run inside an Azure region, one of the datacenters that Microsoft has all around the world.
So where does Azure Arc fits into this picture?
If we bring Azure Arc into the picture, we can bring resources that are not running on Azure to the Azure control plane and by doing that we can start using all services on top of the Azure Resource manager to secure, monitor, protect, … these resources. These resources can be running in your own datacenter or even at one of the other cloud providers!
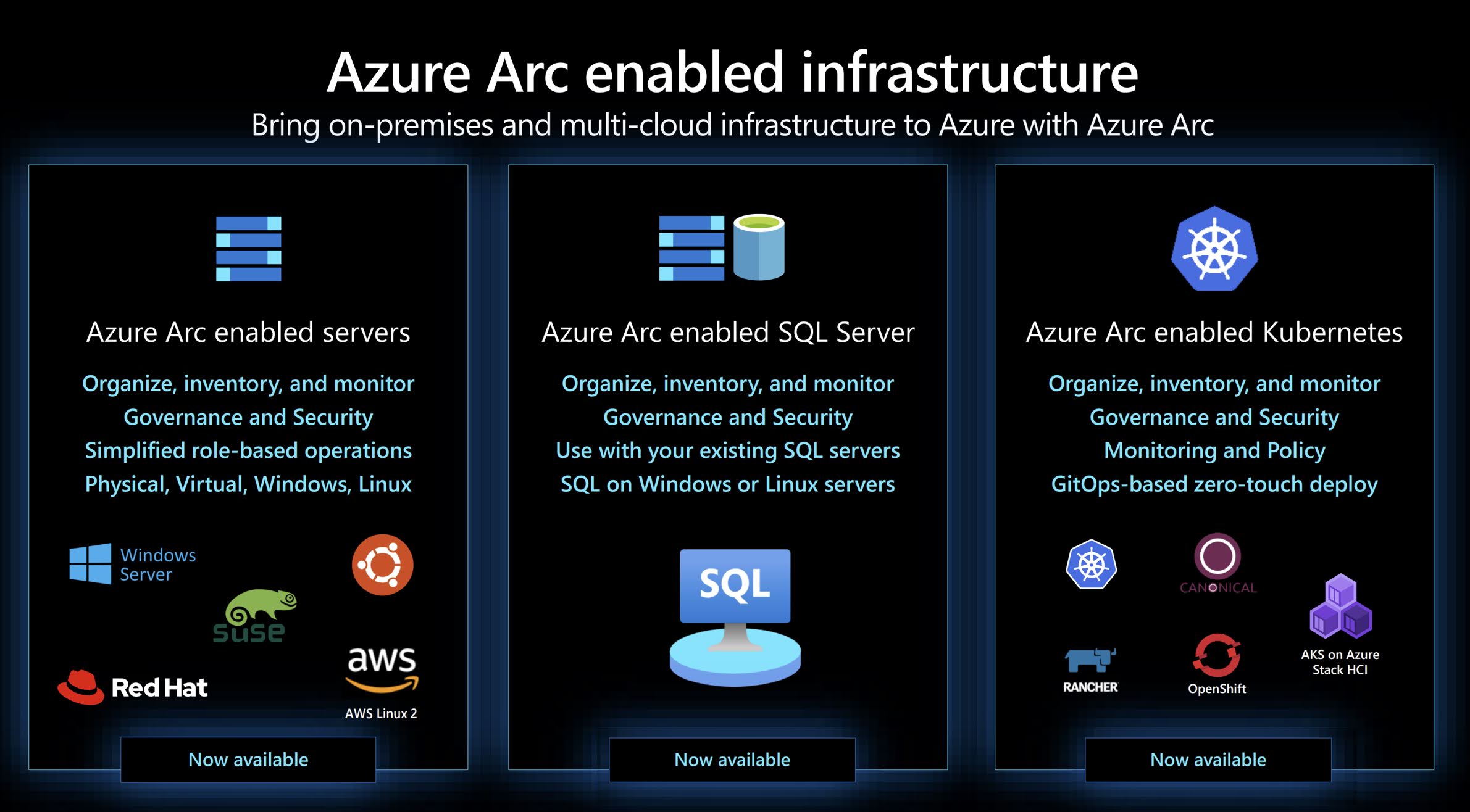
Today, Azure Arc allows you to manage the following resource types hosted outside of Azure:
- Servers - both physical and virtual machines running Windows or Linux.
- Kubernetes clusters - supporting multiple Kubernetes distributions.
- Azure data services - Azure SQL Managed Instance and PostgreSQL Hyperscale services.
- SQL Server - enroll instances from any location with SQL Server on Azure Arc-enabled servers.
I think this really is a game changer as it allows you to start using all the knowledge, experience and tooling you’ve build up on Azure outside the Microsoft datacenters.
The future looks bright…