The Web Application Project is configured to use IIS. Could not find the server 'https://localhost/SampleApp' on the local machine. Make sure the local IIS server has been configured to support secure communications.
After configuring a new Windows 10 machine, I loaded my first solution to start fixing some bugs. However the web project in my solution failed to load with the following error message:
C:\projects\SampleApp/WebUI.csproj : error : The Web Application Project SampleApp.WebUI is configured to use IIS. Could not find the server 'https://localhost/SampleApp' on the local machine. Make sure the local IIS server has been configured to support secure communications.
Whoops! Seems that I forgot to configure something in IIS. I didn’t enable the SSL binding on my local IIS instance.
Let’s fix this!
- Open up the Internet Information Services(IIS) Manager
- Click on the Default Website
- Click on Bindings… in the Action pane on the right
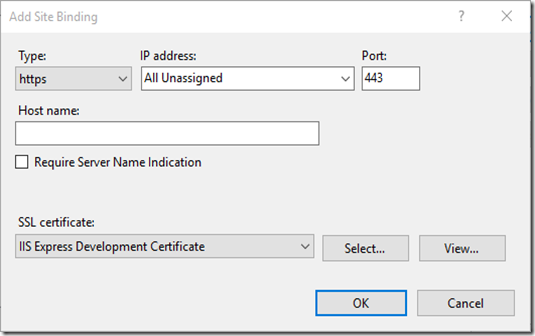
- Click on the Add… button to open up the Add Site Binding dialog
- Specify https in the Type dropdown and choose an appropriate SSL certificate from the list
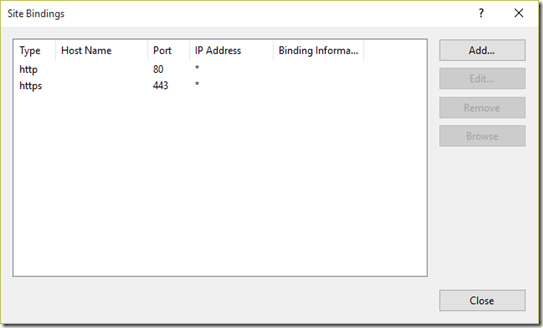
- Click OK to close the dialog. The SSL binding is added to the list
- Click on Close
Now I can reload the web project in Visual Studio without any error…