Looking for a free(!) tool to connect to your Cloud databases? One of the tools I’ve been trying is Toad for Cloud Databases, a free SQL-based tool with the familiar look and feel of Toad, which enables users to use SQL(yes indeed SQL) with a set of non-relational databases, including Hadoop (Hbase & Hive), Cassandra, MongoDB, SimpleDB, and Azure Table Services.
How does it work?
There are two key components to Toad for Cloud Databases:
- Toad client: Use it to access Cloud/NoSQL databases via SQL statements.
- Data Hub: It translates SQL statements submitted through the Toad client into a language understood by the Cloud database, and returns results in the familiar tabular row and column format.
Installation
You can download it from the following location(you’ll have to register first): http://toadworld.com/Freeware/ToadforCloudDatabasesFreeware/tabid/842/Default.aspx
Run the installer after downloading has completed.
Get started
- Start the Toad for Cloud Databases client. Once the client is loaded you’ll see the Data Explorer on the left.
- Right click on the Embedded Data Hub and choose Map Data Source…
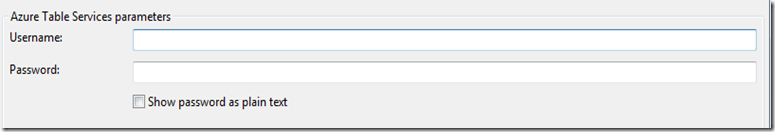
- The Map Data Source wizard is loaded. Specify a Data source name and choose the appropriate Data source type(we’ll choose Azure Table Services).
- Specify the credentials to connect to your data source and click OK to complete this step.
- The data source is added to the Tree view.
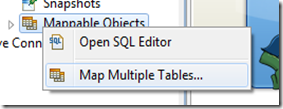
- However before we can start doing something, we have to create a mapping first. Right click on the Mappable Objects and choose Map Multiple Tables…
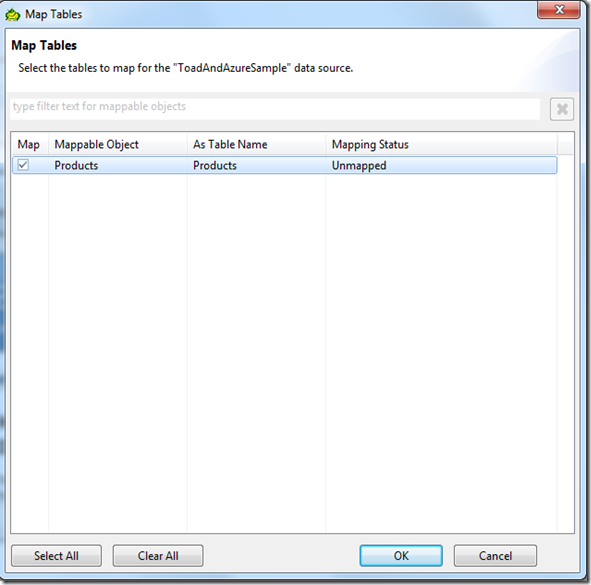
- The Map Tables screen is loaded. Select the Table you want to map and click OK.
- The tool will create a Table for us and map all the found columns as can be seen in the Data Explorer Tree view.
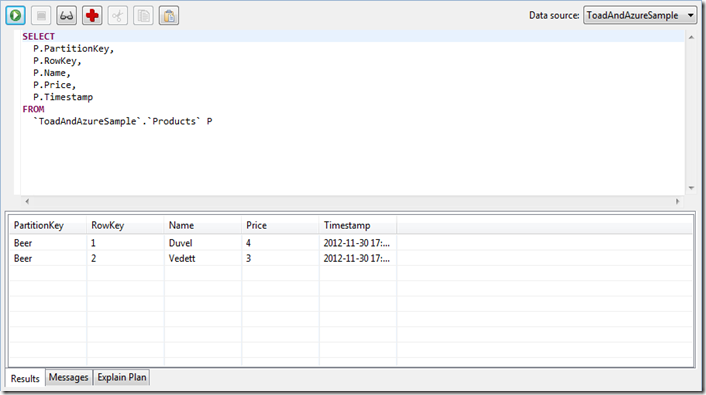
- Now we can right-click on the created table and start writing SQL by choosing Open SQL Editor.
- A SQL Editor is opened and you can write and execute SQL statements.
- That’s it!